For your website to be more visible and to receive more organic traffic, search engines must efficiently index and crawl it. Crawl errors can have negative consequences on your website’s search engine rankings and prevent your content from showing up in search results.
However, there’s no need to panic. You can access various valuable insights like how search engines crawl & index your website and Crawl Errors in Google Search Console. In this blog post, we will discuss effective strategies to fix crawl issues in Google Search Console to ensure that your website receives optimal visibility and indexing.
What Do We Mean by Crawl Errors?
When search engine bots have trouble accessing and indexing particular pages or areas of your website, this is known as a “crawl error.” These mistakes might reduce the visibility of your website in search engine results pages (SERPs) and reduce the organic traffic it receives. When it comes to these crawl problems, Google Search Console offers helpful insights that make it possible for you to quickly discover and fix them.
But, How We Can Identify Crawl Errors?
The first step to fix crawl errors is to identify the errors. To get an idea of your website-related crawl errors in Google Search Console, first, log in to your Google account and verify your website authority in GSC. Google Search Console provides a dedicated “Coverage” report that displays information about crawl errors. Mainly, crawl errors can be divided into 2 sections:
- Site Errors: These errors indicate problems that prevent search engines from accessing your entire website. This includes DNS errors, server connectivity issues, or robots.txt file misconfigurations.
- URL Errors: These errors occur when search engines face problems crawling specific pages on your site. It can be caused by various factors such as server errors, broken links, or URL redirects.
Common crawling issues and ways to fix them:
Server Errors (5xx)
Server errors indicate an issue on the server hosting your website. It means that the server encountered an internal error while trying to process the request. Common server errors include 500 (Internal Server Error), 502 (Bad Gateway), and 503 (Service Unavailable).
Resolution:
- Check your server logs to identify any specific errors or patterns that may be causing server issues.
- Make sure your server is functioning effectively. If there are any server-related problems, get in touch with your hosting provider.
- Ensure that your server can handle the crawl load and respond with appropriate status codes.
Soft 404 Errors
Soft 404 errors occur when a page that doesn’t exist returns a “200 OK” status code instead of a “404 Not Found” code.
Resolution:
- Find pages that cause soft 404 errors and check their status codes. Make sure a page that doesn’t exist produces a “404 Not Found” response code.
- For pages that do exist, verify that they return the appropriate status code and appropriate information.
- Design unique error pages that alert users when a page is missing or has been deleted. Include links to the appropriate pages or parts of your website.
- Check to see whether soft 404 error pages are being sent to irrelevant or unrelated pages. Rectify any incorrect redirects and reroute visitors to suitable pages.
Redirect Errors (3xx)
Redirect errors occur when there are issues with URL redirects. Common redirect errors include redirect chains or loops. Incorrectly implemented redirects can lead to crawl errors. Ensure that all redirects on your website are properly implemented and functional. It helps search engines reach the desired content effectively.
Resolution:
- Analyze your website’s redirect setup, ensure there are no unnecessary redirects, and fix any redirect loops.
- Use 301 redirects for permanent moves and 302 redirects for temporary ones.
- Fix any broken or incorrect redirects by updating them to the appropriate URLs.
Not Found (404) Errors
These errors occur when the requested page is not found on your website. Review the URLs triggering these errors and fix broken links or update the page URLs accordingly.
Resolution:
- Ensure that all internal links on your website point to valid and existing pages. Check for any broken links and update or remove them accordingly.
- If a page has been permanently removed or its URL has changed, use 301 redirects to guide visitors and search engines to the appropriate page.
URL Errors
When search engines have trouble accessing particular URLs on your website, URL errors happen. It means that the submitted URL is not being indexed by search engines.
Resolution:
- Verify that the robots.txt file on your website is not preventing search engines from accessing relevant pages. If required, modify the file to enable relevant content to be indexed by search engine crawlers.
- Verify that the URLs identified as errors are correct and accessible. Correct any spelling or formatting problems in the URLs if necessary.
Access Denied (403) Errors
This error indicates that search engine crawlers are being blocked from accessing specific pages or directories.
Resolution:
- Ensure that your website’s robots.txt file allows search engines to crawl relevant content.
- Check if there are any specific access restrictions in place, such as IP-based restrictions or user-agent restrictions, and modify them accordingly.
To minimize crawl errors in the long term and maintain a healthy website structure, adopt the following best practices:
XML Sitemap
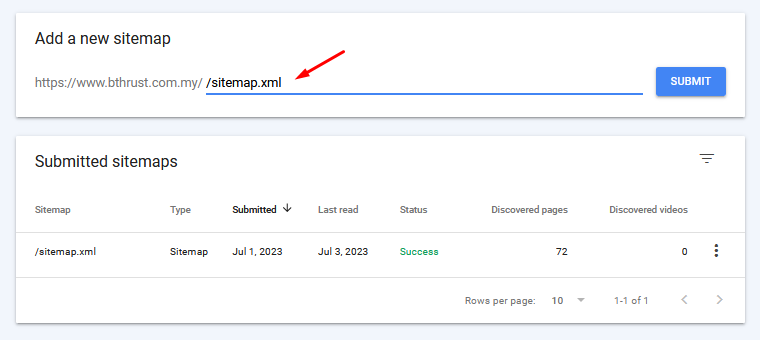
Create and submit an XML sitemap to Google Search Console. This helps search engines understand the structure and hierarchy of your website, discover and index your website’s pages more efficiently, and improve crawling efficiency.
Internal Linking
Use a strong internal linking strategy to make sure that search engine bots can quickly find all of your website’s essential pages. By tying relevant content together, orphaned pages can be avoided.
Page Speed Optimization
To stop search engine bots from timing out during the crawling process, optimise the speed of your website’s loading. To increase page performance, reduce the amount of code on the page, compress the pictures, and use caching. Make sure your website is quick, responsive, and simple to use. Crawl errors may grow due to poor website performance.
Monitor Changes and Updates
Keep a careful eye on the crawl errors whenever you make big changes to your website, such as redesigning or restructuring, to discover any problems that may develop as a result of these changes.
Regularly Monitor Crawl Errors
Check the Coverage report regularly in Google Search Console to find any new crawl errors and fix them right away.
Conduct Thorough Website Audits
To find and resolve any possible crawlability issues, such as broken links, duplicate content, or erroneous URL structures, conduct detailed website audits.
Conclusion
Fixing crawl errors in Google Search Console is vital for maintaining a healthy website and ensuring enough visibility in search engine results. A great user experience for your visitors and a seamless crawling process for search engine bots will result from routine monitoring and following recommended practices. To ensure the ongoing success of your website in the fiercely competitive online environment, be careful and periodically monitor Google Search Console for any crawl issues.




